Ficin shows promise in wound-healing activity
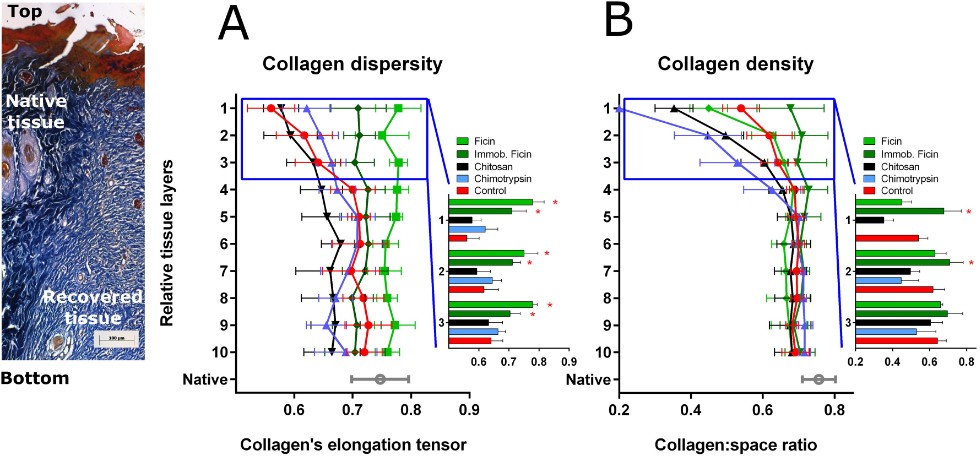
Figure: Evaluation of collagen's elongation tensor (A) and collagen density (B) on histological sections of wound healing tissues from infected wounds either untreated (control) or subjected to various treatment scenarios including soluble Ficin (1 mg ml−1), immobilized Ficin (75 mg ml−1), chitosan (75 mg ml−1) and chymotrypsin (1 mg ml‐−1) as a reference. The biopsy specimens were taken on the 15th day after injury.
A paper saw light in International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.
Co-author, Associate Professor (Department of Genetics, Kazan Federal University) Airat Kayumov explains, “One of the main problems that doctors face when treating skin wounds and burns in people with weakened immunity is the appearance of a biofilm formed by conditionally pathogenic microflora (Staphylococcus aureus and S. epidermalis, Micrococcus, Pseudomonas). In biofilms, bacteria are immersed in a matrix - a multicomponent high molecular substance similar to jelly, and antibiotics cannot penetrate it, so healing is slowed down.”
Three years ago, researchers from Kazan University and Voronezh University found out that ficin, a proteinase from fig tree sap, is capable of destroying the matrix of staphylococcal biofilms, so the combination of ficin with antimicrobial drugs will increase their effectiveness.
Enzymes are substances of a protein nature, so they are unstable during storage, and are also sensitive to heat. To solve these problems, the researchers decided to anchor the enzyme on an insoluble natural polymer, chitosan.
«The method of immobilizing ficin on chitosan, a derivative of chitin, a natural polymer that is the basis of the shell of crustaceans and insects, was developed by our colleagues from Voronezh University. During immobilization, the enzyme attaches to an insoluble carrier so that it can exchange substrate and product molecules with the solution,» says the interviewee.
The advantage of chitosan in comparison with many other natural polymers is its biological compatibility and antimicrobial, antifungal and analgesic activity. In the future, it can be used as a carrier for the immobilization of other enzymes used in biomedicine.
«Treatment of model wounds of laboratory animals with immobilized ficin showed that they are cleared of bacteria and heal faster. And what is most interesting: the structure of the newly formed tissue treated with ficin has characteristics that are closest to the original, intact tissue,» emphasized Kayumov.
The next step is to create bandages with ficin and antimicrobial preparations.
Anti-biofilm and wound-healing activity of chitosan-immobilized Ficin
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0141813020343841
Source text: Larisa Busil
Photo: Airat Kayumov
Translation: Yury Nurmeev