Research
The study of the molecular mechanisms of programmed cell death of T-lymphocytes during the development of the autoimmune process
Skibo Y.V., Abramov S.N., M. Tikhomirova M.V., Biktagirova E.M., Abramova Z. I.
Hypothesis: in the presence of aberrant cells that can become oncological, as well as cells infected with various pathogens, T-lymphocytes are activated. Under the influence of various factors, activated T cells can be directed against the body's own cells, which leads to allergic and autoimmune diseases, such as asthma, multiple sclerosis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. One of these factors may be a violation in the implementation of the cell death program, which is represented by several types. And within the framework of this project, we study the main types as apoptosis, autophagy, and LC3-associated phagocytosis, using the example of bronchial asthma (BA) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Targets:
- To evaluate the main indicators of autophagy in T-lymphocytes of patients with BA and SLE;
- Determine the level of gene expression of Rubicon, Beclin-1, UVRAG, VPS34, responsible for the formation of LAPosomes in T-lymphocytes of patients with BA and SLE;
- To characterize the main morphological and biochemical parameters of apoptosis in T-lymphocytes of patients with BA and SLE;
- Conduct a correlation analysis of the data and describe the possible mechanisms leading to autoimmune burden.
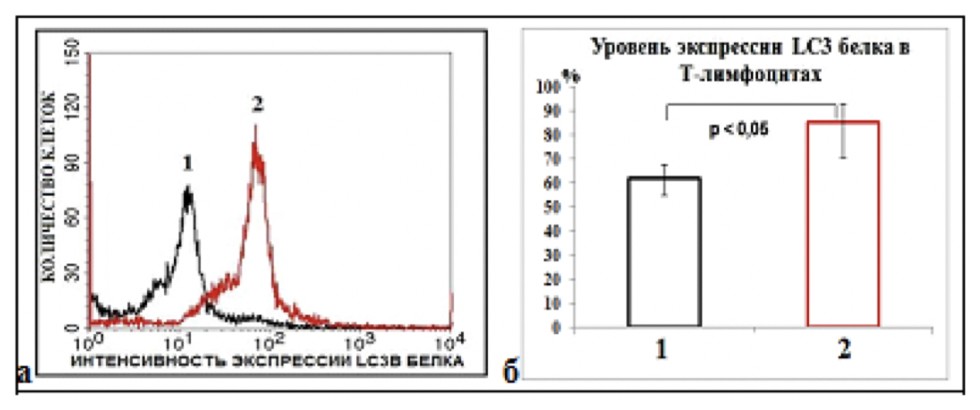
Results: a weak manifestation of apoptosis of T-lymphocytes in patients with bronchial asthma in vitro was established. Also in T-cells of patients with asthma, activation of autophagy is shown: in the group with a mild form of the disease, autophagy leads to the death of T-lymphocytes along the path of programmed cell death of type II. In the group with severe asthma, autophagy promotes cell resistance to death and their long-term functioning. We found a weak manifestation of LC3-associated phagocytosis, which, together with inhibition of apoptosis in the final stages, may be the cause of the appearance of autoantigens and the development of an autoimmune response. In addition to ultrastructural, there are molecular changes that determine the type of autophagy (canonical or LAP), the study of which will be the goal of further research.
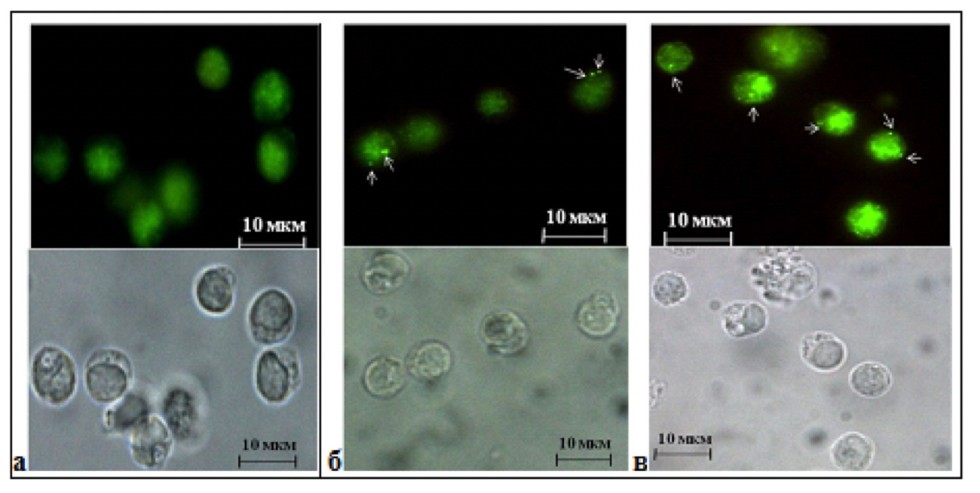
| Fig. 1. Representative micrographs of T-lymphocytes of a healthy donor and patients with mild and severe forms of bronchial asthma after 3 days of cultivation. (a) The absence of expression of the LC3B protein in T-lymphocytes of a healthy donor has been established; (b) Expression of LC3B protein on autophagosomes in T-lymphocytes in patients with mild asthma; (c) LC3B protein expression on autophagosomes in T-lymphocytes of patients with severe ABA. |
|
The effect of the risk of allele A polymorphism rs200395694 on the regulation of the MEF2D gene and alternative splicing in patients with SLE
Abramov S.N., Kozyrev S.V.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is one of the most severe human autoimmune diseases. The incidence of SLE in women is up to 10 times higher than in men. Ethnicity is associated with prevalence, disease progression and mortality. These facts suggest that genetic predisposition can play an important role in the appearance and development of SLE. We used a new generation sequencing method to search for new polymorphisms that may play a role in the heritability of the disease. After analyzing the data, we found a new polymorphism rs200395694 located in the MEF2D gene encoding the transcription factor MEF2D associated with SLE in Swedes. The regulatory potential of rs200395694 was investigated using EMSA and luciferase reporter analysis and showed allelic differences in both protein-DNA binding and reporter transcription.
MEF2D gene splicing was studied by PCR and qRT-PCR using RNA isolated from PBMC and various cell lines.
The two main isoforms a1 and a2 were found in PBMC, THP-1, K562, and Daudi, but only the a1 transcript was found in the Jurkat, HeLa, and HEK293 T cell lines. Minigens with different genotypes were used to evaluate the effect of polymorphism on splicing. There was no difference between the alleles for the a1 isoform in any of the analyzed cell lines, while the a2 isoform was significantly suppressed by the rare allele A.
Conclusion: we identified the association of the regulatory variant rs200395694 with SLE in Swedish patients. The risk allele affects gene regulation and also inhibits splicing of the alternative MEF2D transcript.
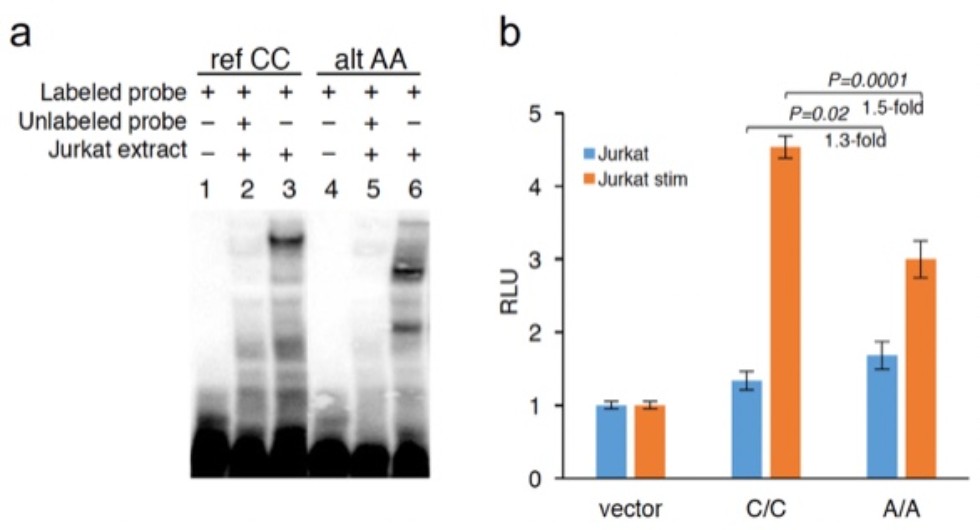
Binding and regulatory potential of rs200395694 alleles. (a) EMSA results with nuclear extract from Jurkat cells. (b) Luciferase reporter assay performed in Jurkat. Bars represent mean values +/- SD. RLU, relative light units. Statistical analysis was done using an unpaired t test.
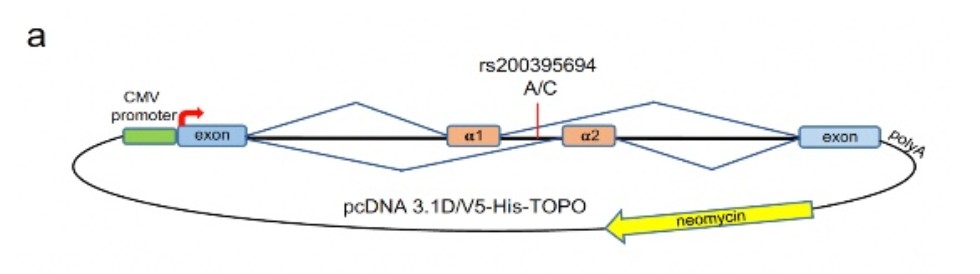
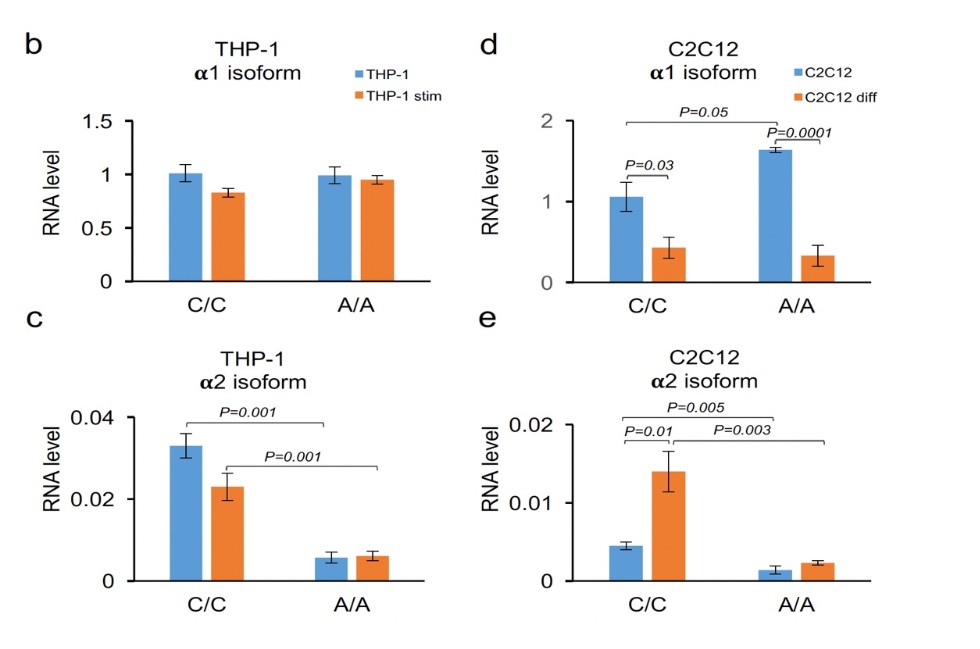 | Analysis of alternative splicing with minigenes. (a) Minigenes with alternative alleles were cloned into pcDNA3.1 vector between the CMV promoter and the polyadenylation site. (b-e) Levels of alternative isoforms transcribed from minigenes transfected into THP-1 cells (b,c) and C2C12 cells (d,e) were measured by quantitative RT-PCR. THP-1 cells were stimulated with 100 ng/ml of LPS and 10 ng/ml of interferon gamma for 12 h. C2C12 cells were differentiated with 2% horse serum for 64 hr. Bars represent mean values +/- SEM. |
Research of new effective antitumor medicinal tropone-containing substances and modeling of their activity
Boumber Y., Deneka A., Topchu Y., Mazitova A. Biktagirova E., Davletshin D., Khusainova E.
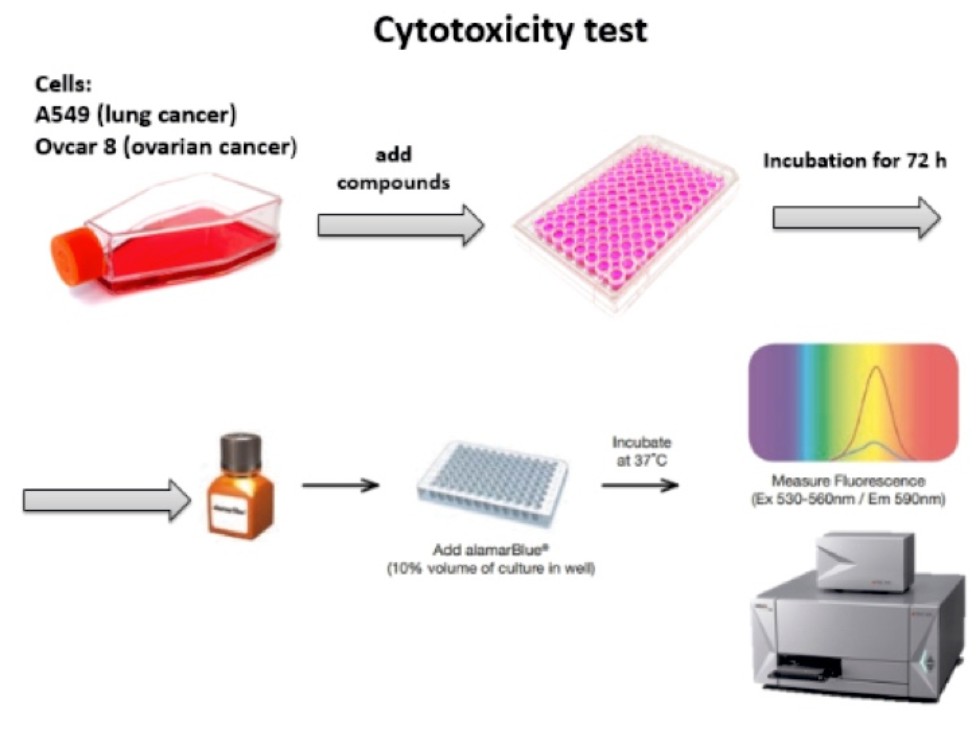
In the framework of cooperation with the Center for Science and Research, RAS, the cytotoxicity of troponic substances on tumor cell lines is being studied.
The tropolon-containing substances were provided by Yu.A. Sayapin and Gusakov E.A. The study of cytotoxicity is carried out within the Research Laboratory of the Molecular Principles of Therapy and Pathogenesis of Tumor Diseases. Total cytotoxicity is characterized by the same sensitivity to the action of a substance, regardless of the cell type.
Substances that exhibit cytotoxic properties at low concentrations are selected for further investigation of the mechanism of action on the (tumor) cell.
Cell viability studies are performed using Alamar Blue reagent. The method for assessing cell viability is based on the conversion of a non-toxic water-soluble resazurin to a fluorescent substance resorufin. on the conversion of non-toxic water-soluble resazurin into a fluorescent substance resorufin. |
|
Employees filed an application for a joint grant of the Russian Science Foundation, in case of support, it is planned to conduct a series of experiments on toxicity studies in mouse models.
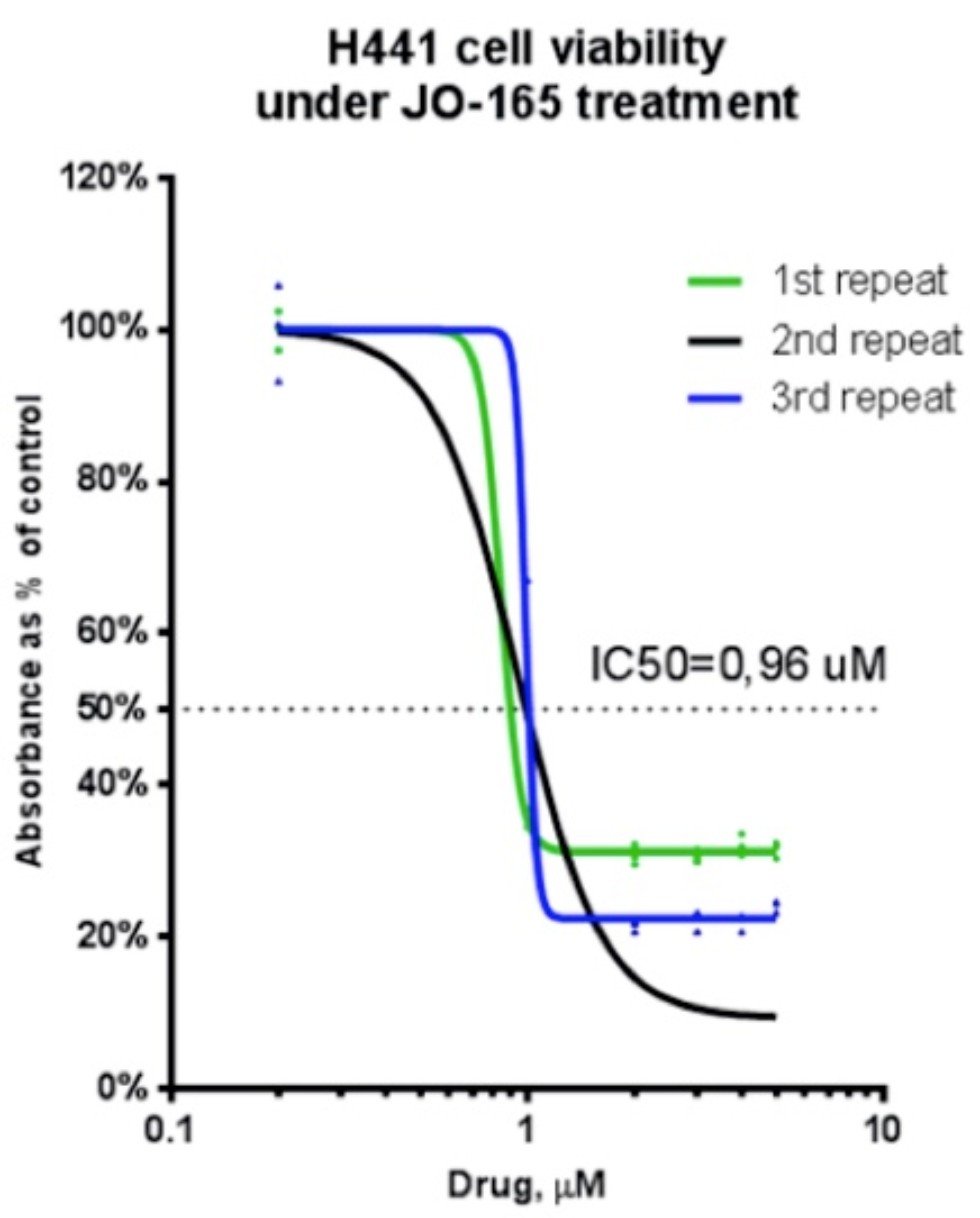 | Effect of compound JO-165 on H441 cell viability. The cells at a initial density of 0.15×10⁴ per well were treated with compound JO-165 in a final volume of 100 ul RPMI-1640 complete medium containing 10% FCS for 72 h. Data are represented as the mean and SEM (error bars) for n=3 |
The study of the role of protein Musashi2 in the regulation of the signaling pathway of VEGFR2-VEGFA and related target proteins in lung cancer
Boumber Y., Deneka A., Topchu Y., Mazitova A.
Using metastatic mouse and human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines, as well as comparing NSCLC cell lines with high and low metastatic potential obtained from transgenic KrasLA1 / + / p53R172HDG / + mouse tumors, it was found that one of the most persistent phenotypic features of metastatic cells was increased protein levels of Musashi-2 (MSI2), which plays an important role in invasion and metastasis of NSCLC in vitro and in vivo. A previous analysis of the proposed signaling pathway and screening of relevant MSI2 targets revealed a number of proteins associated with the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMF) —type TGF-β receptor (TGFBRI) type I, SMAD3, claudins, and the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR2).
The three main fundamental tasks are of considerable scientific interest in the planned study.
- To study the role of Musashi2 protein in the regulation of the signaling pathway of VEGFR2-VEGFA and related target proteins in lung cancer (We first showed the regulation of the path of VEGFR2-VEGFA Musashi2).
- Determine the role of the interaction between the Musashi2 protein and the VEGFR2-VEGFA pathways in the context of targeted therapies affecting these proteins and MSI2 (the role of MSI2 in regulating the response to the effects of VEGF / VEGFR2 inhibitors cabostiniband pazopanib).
- Identify partner proteins that interact with Musashi-2 and are critical for the growth and development of NSCLC.
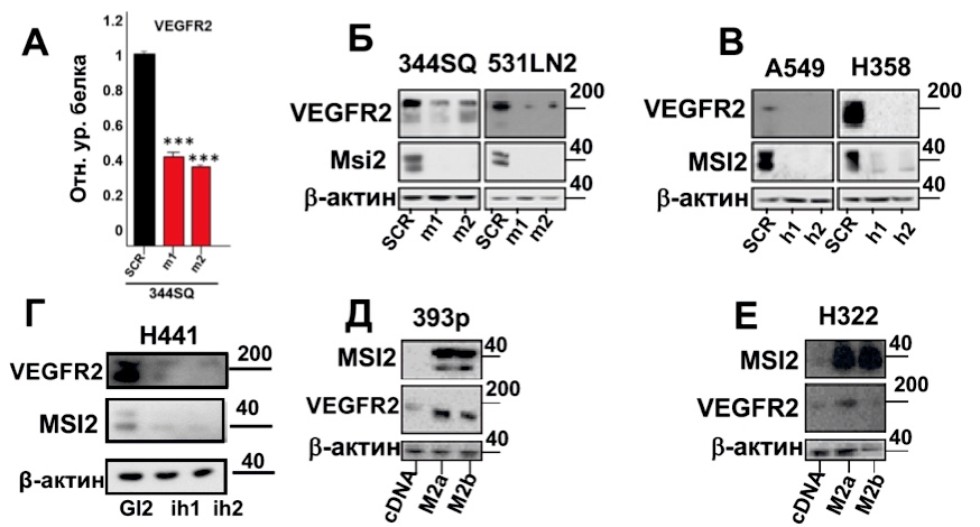
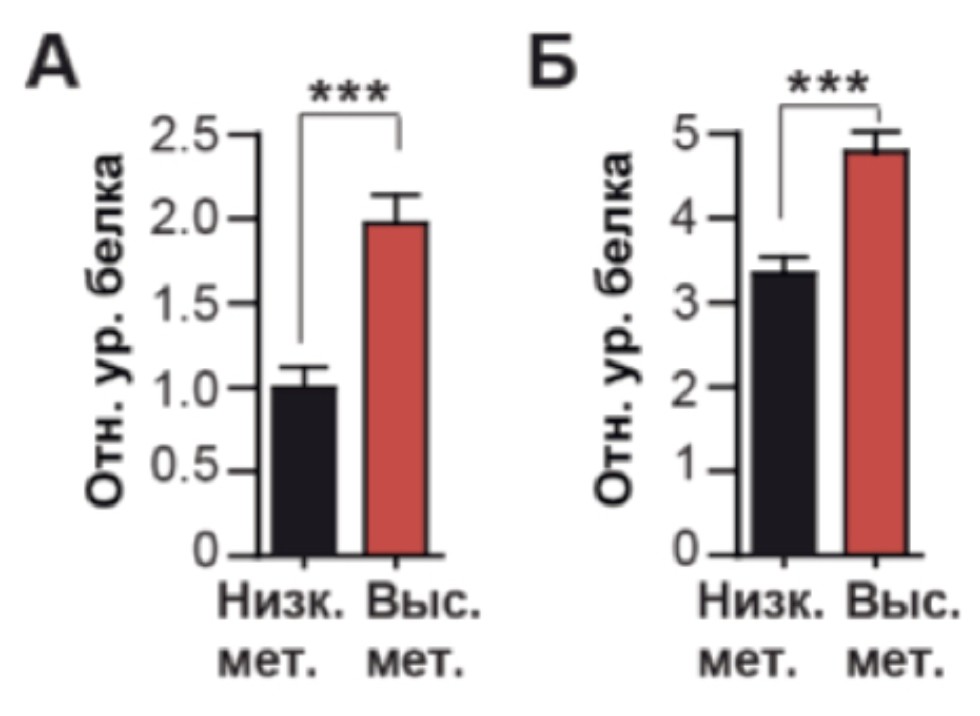
Regulation of VEGFR2 by MSI2 protein. A) VEGFR2 protein level in shRNA 344SQ cell line induced by decrease in MSI2 levels ('m1,' m2), and in negative control (SCR), assessed using the RPPA method; B, C, D: Western blot analysis of VEGFR2 level in murine and human NSCLC cell lines with shRNA induced by decrease in the levels of MSI2 ('m1 and' m2, 'h1 and' h2) and negative control (SCR), as well as miRNA by MSI2 knockdown ( ih1, ih2) and GL2 negative controls in the H441 cell line; D, E: Western blot analysis of VEGFR2 level in the human H322M cell line with over-expressed ('M2a,' M2b) MSI2 and control (cDNA). The data obtained were statistically analyzed using the Mann-Whitney test * p <0.001
| MSI2 levels are elevated in the NSCLC. A) Densitometry of the MSI2 protein level in 7 non-invasive 7 metastatic mouse NSCLC cell lines; B) The MSI2 protein level in patient tissue samples (22 normal and 123 tumor), assessed by RPPA. The data obtained were statistically analyzed using the Mann-Whitney test; *** p <0.001. |
The research was funded by d by RFBR according to the research project № 18-44-160004
Testing of combined SRC family kinases and heat shock protein 90 inhibition in lung cancer
Deneka A., Mazitova А., Topchu Y.
The goal of this proposal is to understand how changes occurring during metastasis of non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) promote aggressive phenotypes and drug resistance, and come up with better ways to treat lung cancer. NSCLC is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the world, and metastasis are the most common cause of death in lung cancer patients. Despite many advances in therapeutic management, the five-year survival rate for lung cancer remains at around 16% of diagnosed cases.
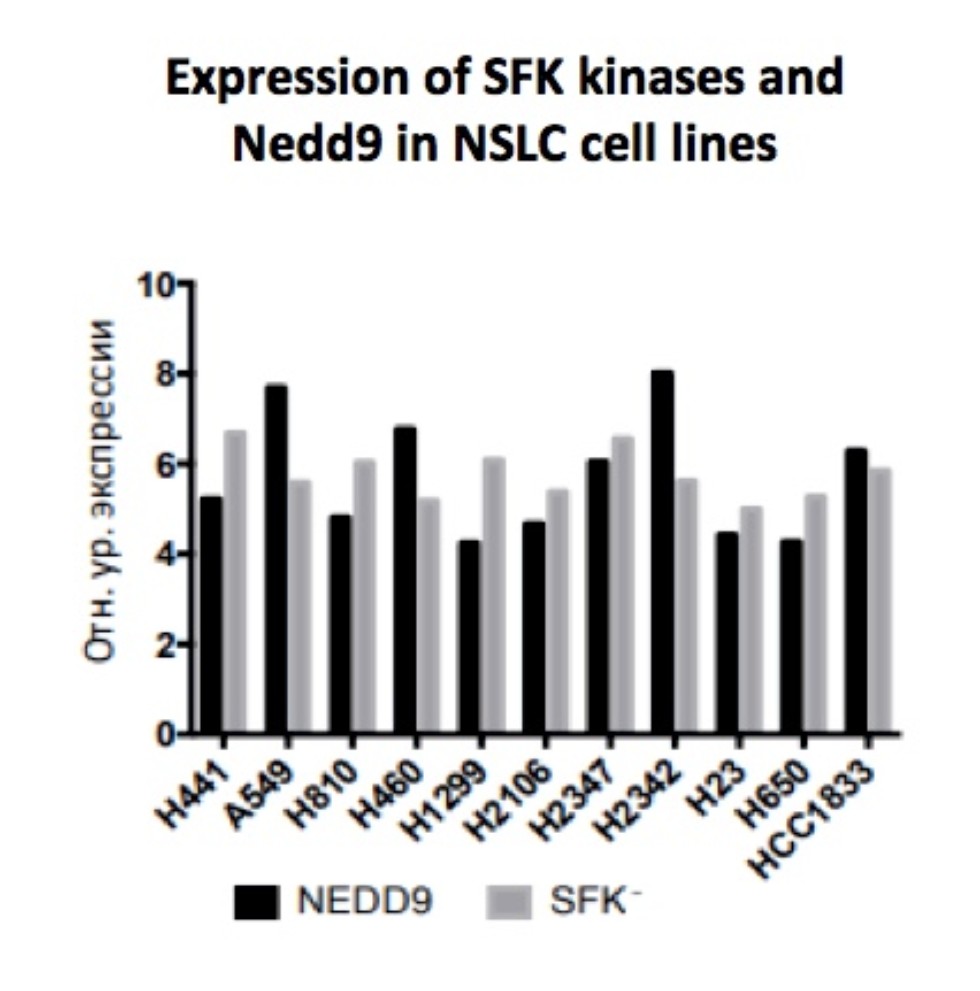
Elevated activity of SRC family kinases (SFKs) and heat shock protein (HSP) 90 are both associated with cancer progression, invasion, tumor angiogenesis and drug-resistance, and both are targets of inhibitors currently in clinical development for the treatment of several cancers, including lung cancer. The scaffolding protein NEDD9 binds SFKs and controls their activity, and has very recently been defined as a factor regulating drug response and prognosis in lung cancer. The first evaluation of the efficacy of dual inhibition of SFKs and HSP90 lung cancer in the context of NEDD9 expression will be performed. This proposal potentially will reveal novel biological mechanisms, that contribute to growth, metastasis and chemotherapy response of tumor cells in lung cancer setting.
The first evaluation of the efficacy of dual inhibition of SFKs and HSP90 lung cancer in the context of NEDD9 expression will be performed. This proposal potentially will reveal novel biological mechanisms, that contribute to growth, metastasis and chemotherapy response of tumor cells in lung cancer setting. The research was funded by RSF according to the research project № 18-75-00104 |
|
Investigating the role of autophagy in aggressiveness and drug resistance of epithelial ovarian cancer
Gabbasov R., Mazitova А., Biktagirova E., Mingazova L.
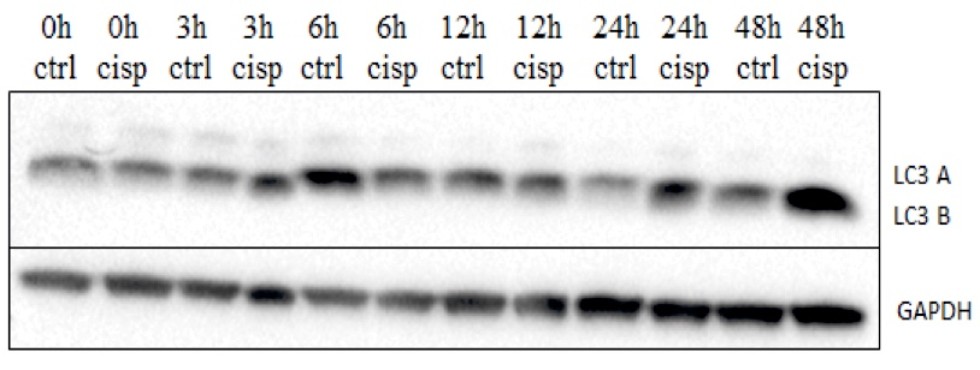
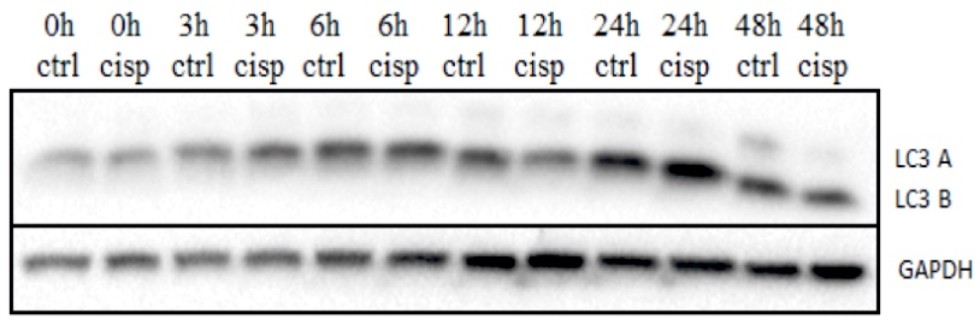
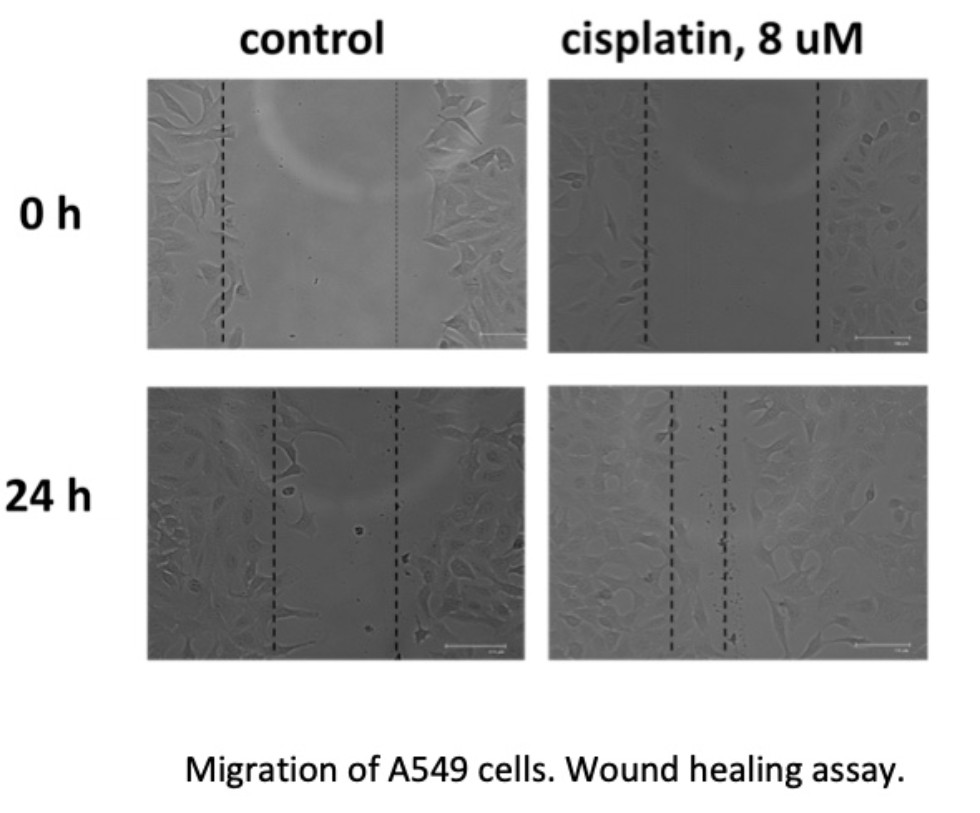
High-grade serous epithelial ovarian carcinoma (HGSOC) is the deadliest gynecologic malignancy, which often develops drug resistance. According to published data, HGSOC cells induce autophagy in response to cisplatin treatment as well as in process of development of cisplatin resistance. Additionally, treatment of epithelial cancer cells with sublethal doses of cisplatin may increase their aggressiveness. At the same time, reports on expression of autophagy markers in clinical specimens of HGSOC are contradictory. The current project aims to investigate the role of autophagy in adaptivity of HGSOC cells to cisplatin, as well as to address the possibility of association between autophagy marker expression with clinical manifestation of HGSOC.
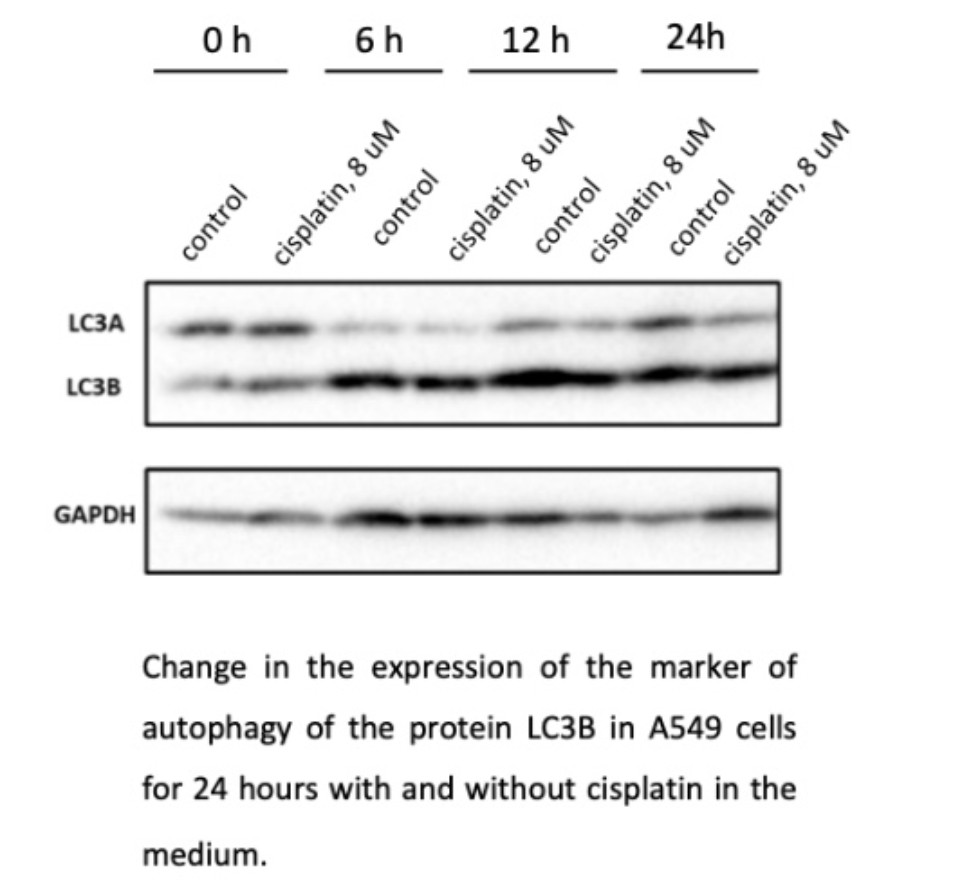
Changes in the expression of the autophagy marker LC3B protein in CaOV-3 cells within 48 hours with and without cisplatinin the medium.
Changes in the expression of the autophagy marker LC3B protein in OVCAR-8 cells within 48 hours with and withoutcisplatinin the medium. |
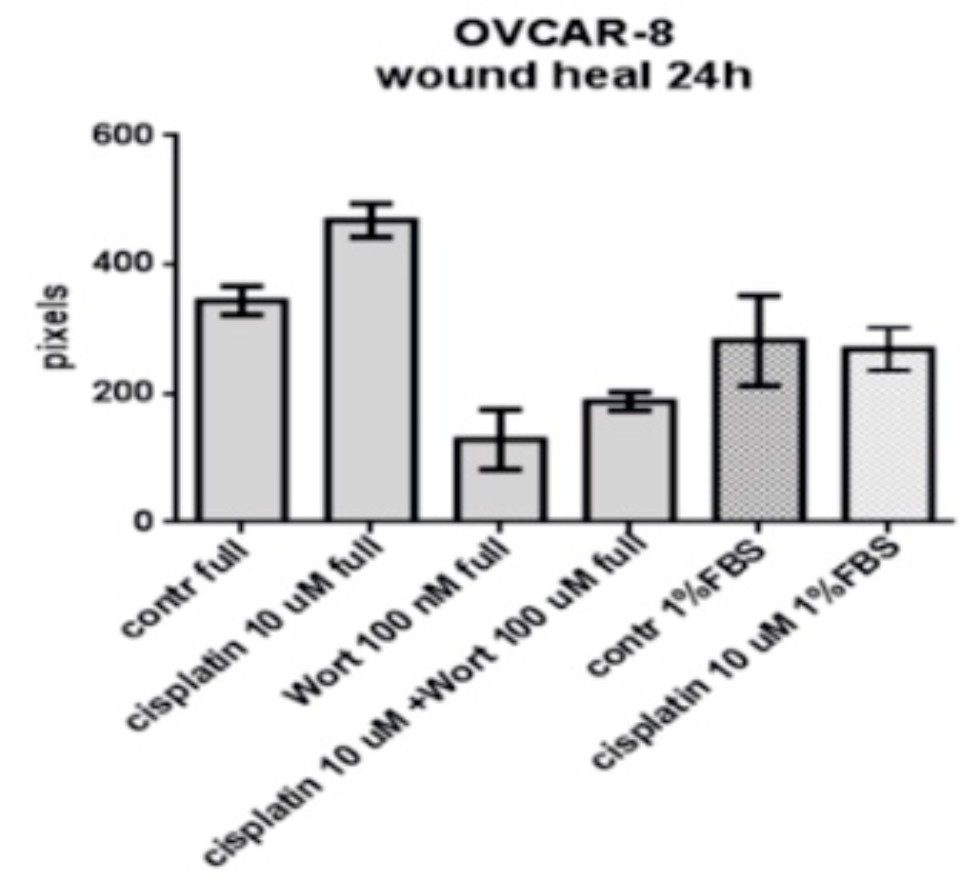
The rate of migration of OVCAR-8 cells in the monolayer within 48 hours in the presence and absence of cisplatinand an inhibitor of autophagy of wortmaninin the medium. |
The research was funded by RSF according to the research project 18-315-00317
Investigating the role of autophagy in development of epithelial to mesenchymal transition and drug resistance in non-small cell carcinoma cells
Gabbasov R., Mazitova А., Biktagirova E., Topchu Y.
Cisplatin resistance is an important problem in context of non-small cell lung carcinoma treatment. Available data indicates that epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is among factors bolstering development of cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). Besides that, drug resistance in malignant tumors is often followed by enrichment of cancer stem cell (CSC) population within tumors. Based on literature research, we hypothesize that EMT and development of CSC features in NSCLC cells in response to cisplatin treatment may be mediated by autophagy. Our project is aimed to investigate the role of autophagy in adaptivity of NSCLC cells to cisplatin treatment through induction of EMT and CSC-like phenotype.
The current project addresses the following questions:
1) Does autophagy regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition as a mechanism allowing adaptation of NSCLC cells to cisplatin treatment and development of cisplatin resistance?
2) Does autophagy play role in development of cancer stem cell-like phenotype by cisplatin-resistant NSCLC cells?
3) Is autophagy associated with EMT and general aggressiveness of NSCLC in clinical settings?
 |
|
The research was funded by RFBR according to the research project № 18-015-00495
Effect of targeted kinase inhibitors on ciliary dynamics and cilia-associated signaling
Ilya Serebriiskii, Anna Kiseleva
The primary cilium is a hair-like organelle extended from the cell surface where it plays a role of an antenna for transduction of cellular signals. Mutations of ciliary genes or complete loss of cilia can lead to the development of severe disorders called ciliopathies, including polycystic kidney disease, and take part in the cancer pathogenesis. It was shown previously that several anti-cancer compounds, such as the Aurora-A inhibitor alisertib, EGFR inhibitor erlotinib, and HSP90 inhibitor ganetespib control ciliary dynamics and cilia-associated signaling and the progression of the cilia-related diseases, suggesting that additional drugs may affect these processes. In the present study, we analyzed the activity of 178 kinase inhibitors in controlling ciliary dynamics. As a result, we identified that sunitinib, a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, promotes cilium disassembly and significantly reduces the progression of polycystic kidney disease. Further experiments showed that sunitinib also inhibits cilia-associated Hedgehog signaling by the blocking of Smoothened receptor translocation to the ciliary membrane.
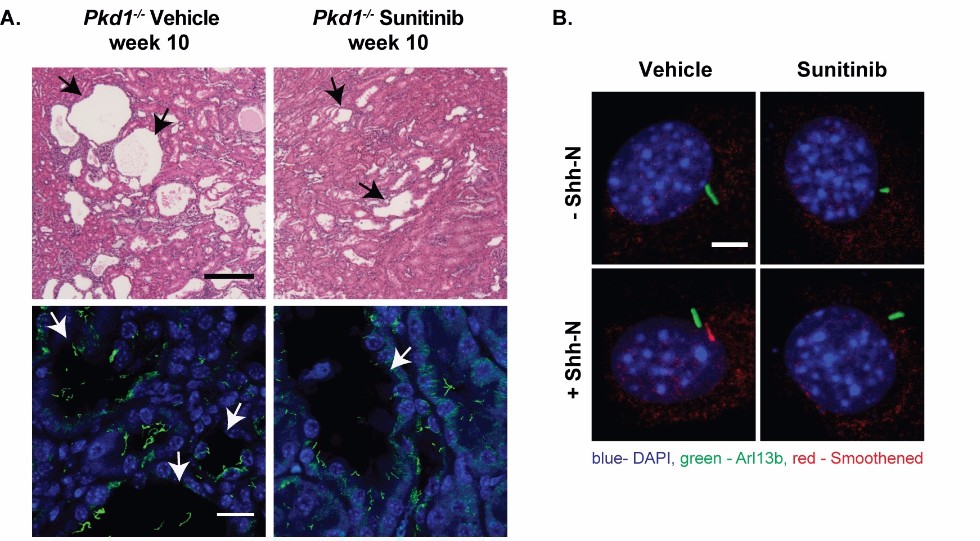
Figure 1. A. Representative H&E and fluorescent images of Pkd1 wt or Pkd1-/- mice treated with vehicle or sunitinib. The results demonstrate a significant reduction of cilia and cyst number after treatment with sunitinib. B. Representative images of Smoothened entry into the cilia of NIH3T3 cells treated with sunitinib and then incubated with or without the Hedgehog specific ligand.
Analysis of expression obtained by NANOSTRING technology using circulating tumor cells and circulating molecules of mRNA
Ilya Serebriiskii, Ramilia Vlasenkova, Yanis Boumber
The basis for the diagnosis of cancer is a biopsy. Unfortunately, a biopsy of the tumor tissue, which is an invasive procedure cannot always be performed. In this regard, it is important to develop non-invasive methods of analysis of tumor markers, which can be used to track the dynamics of the tumor process in real time, such as a liquid biopsy. At the moment, there are several options on the market of technologies for liquid biopsy research. One of these technologies is the NanostringTechnologies platform.
Heat maps of gene expression of circulating mRNA molecules (A) and circulating tumor cells (B) | The Nanostringtechnologies application using bioinformatics methods including: -Analysis of the reproducibility of data obtained using Nanostringtechnology -Analysis of the expression data in circulating tumor cells and circulating mRNA (patients with small-cell and non-small-cell lung cancer) -Constructing a list of gene identifiers for lung cancer The technological process of analysis of expression data in circulating tumor cells and circulating mRNA molecules was developed with using data of patients with small-cell and non-small-cell lung cancer. |
Search for highly selective kinase inhibitors
Ilya Serebriiskii, Grigorii Andrianov, John Karanicolas
Kinases are a significant part of many important signaling cascades and often their disturbed activity is associated with various cancer and inflammatory diseases. In this regard, many scientists believe that the kinases are promising targets for a treatment. However, the drug design approaches of development new promising inhibitors have a number of problems:
1. New promising inhibitors often have complex synthesis schemes that are difficult to reproduce. In turn, it greatly complicates the test of the compound against other target kinases. Consequently, the "chemical space" of current inhibitors is very limited.
2. Because of the ATP-binding pocket is very conservative, there is a problem for a search for highly selective inhibitors. In addition, there are many different conformations of the active states of kinases, which complicates the development of drugs.
To solve these problems, it was decided to use the in silico method, which able to expand the available “chemical” space and find highly selective commercially available compounds.
So purpose of this project is development of a high-performance method for obtaining highly selective commercially available inhibitors for kinases.
Tasks:
- Search for promising compounds that are promising for further optimization and which have an easy synthesis scheme.
- Selection of kinases for which selective inhibitors will be developed
- Optimization of method parameters
- Checking the best in vitro candidates
Results: An inhibitor MC180295 was used as the starting point, which has nanomolar activity with the CDK9 kinase. Based on the synthesis scheme of the compound, the functional groups were replaced to commercially available analogues from the Sigma-Aldrich and enAmine catalogs. After that, combinations of new functional groups were ranked according to a affinity and conservatism of the interaction of the core of the MC180295 with the kinase domain. In the next step, all new compounds with higher affinity than MC180295 were analyzed in complex with CDK11A. Ultimately, only those compounds were selected for which the difference in affinity of CDK9 and CDK11A was significant.
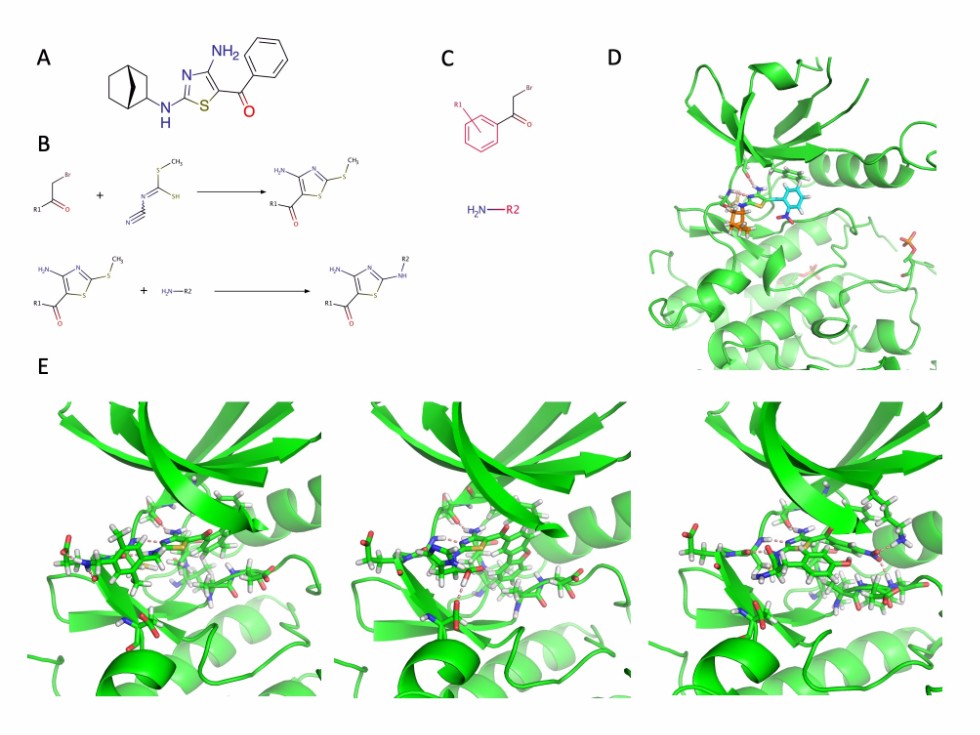
Figure 1. A. The structural formula of the original CDK9 inhibitor is MC180295. B. Two-step synthesis of MC180295. C. Patterns for searching functional groups in the Sigma Aldring and enAmine catalogs. D. The crystal complex of CDK9 and MC180295. E. Three best high-selective inhibitors for CDK9.
Study of interaction of Aurora-A and EGFR inhibitors and their impact on non-canonical signaling pathway of Aurora-A kinase in tumor cells
Alexander Deneka, MD, Junior Researcher
Traditional functions of Aurora-A kinase (AURKA) is the regulation of mitosis and cell kinetic activity. AURKA is overexpressed in multiple tumors leading to aneuploidy by cytokinetyc defects. Aurora A inhibitors such as alisertib let achieve a positive effect in the treatment of cancers that are characterized by overexpression of AURKA, but sometimes cause severe side effects.
 The causes of these side effects are still unclear, and may include newly identified non-canonical functions of AURKA such as control of primary cilia and influence on Ca2 + traffic.
The causes of these side effects are still unclear, and may include newly identified non-canonical functions of AURKA such as control of primary cilia and influence on Ca2 + traffic.
Their inhibition has important physiological significance and explains the deterioration of the phenotype in our mouse model of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) - the most common inherited condition where an important role is violations signaling pathways proteins localized to the primary cilium. Combination therapy with alisertib and erlotinib (inhibitor of EGFR) gives promising results in clinical trials. We explore the non-canonical function of Aurora A inhibitors and their signaling pathways, in particular the combination of erlotinib and alisertib, in a mouse model of ADPKD. Results of in vivo experiments have shown that erlotinib decreases cyst formation and improves the phenotype observed in the monotherapy with alisertib. At the stage of in vitro we clarify the mechanism of this interaction, exploring the target proteins and signaling pathways AURKA and EGFR. We also investigate the effect of combination therapy on the morphology of primary cilia and regulation of Ca2 + traffic.