Researchers functionalized human cells with magnetic nanoparticles
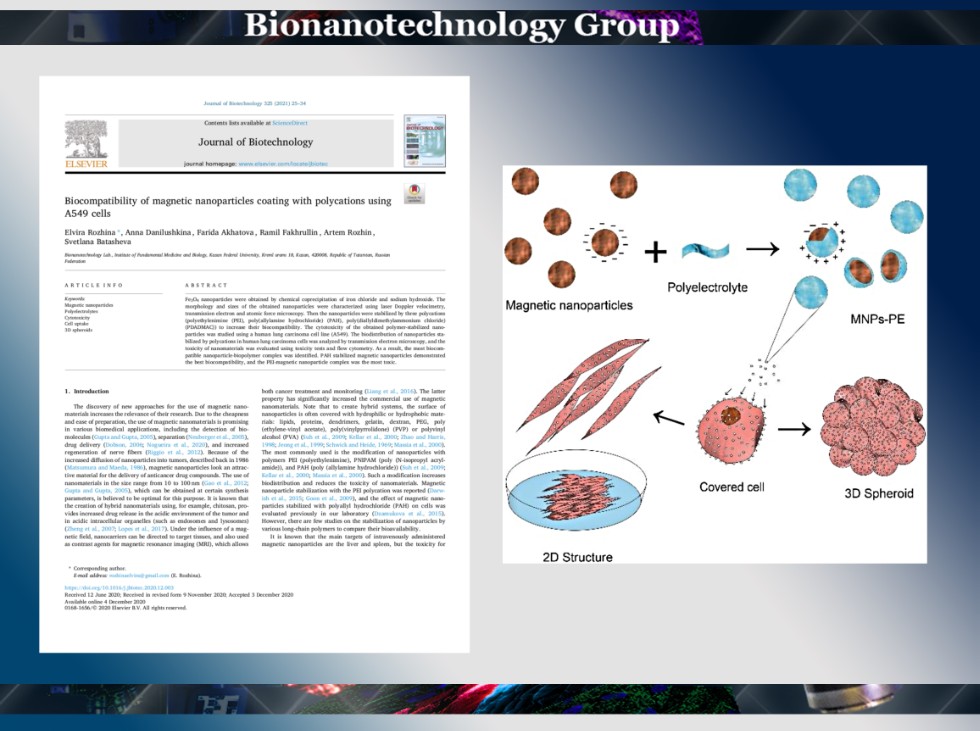
A study evaluating the effects of magnetic nanoparticle coatings on human cells' functional properties became available in the Journal of Biotechnology.
The work is aimed at determining the level of biocompatibility of magnetic nanoparticles coated with various polyelectrolytes. It is known that stabilization of the nanoparticle surface with polymers allows to enhance biodistribution and reduce the material's toxicity. In this work, the obtained nanohybrid systems were characterized by a wide range of diagnostic methods, which did not reveal any decrease in the particles' magnetic properties. The effects of magnetic nanoparticles on cells in monolayer and 3D cultures were evaluated using colorimetric and fluorescence assays. As a result, the particles coated with polyallylamine hydrochloride were the least toxic to both monolayer and 3D cultures. Polyethylamine-coated magnetic nanoparticles showed the highest level of adverse effects. It is noted that the magnetic nanoparticles were attached to the surface of the cell membrane, changing its adhesive properties. Also, their penetration into the cells had little effect on the enzymatic activity. The data obtained indicate a high potential for the application of nanohybrid based on magnetic nanoparticles and polyallylamine hydrochloride in the field of biomedicine.
Title of the article: Biocompatibility of magnetic nanoparticles coating with polycations using A549 cells
Authors: Elvira Rozhina, Anna Danilushkina, Farida Akhatova, Ramil Fakhrullin, Artem Rozhin, Svetlana Batasheva.